What is virtual reality
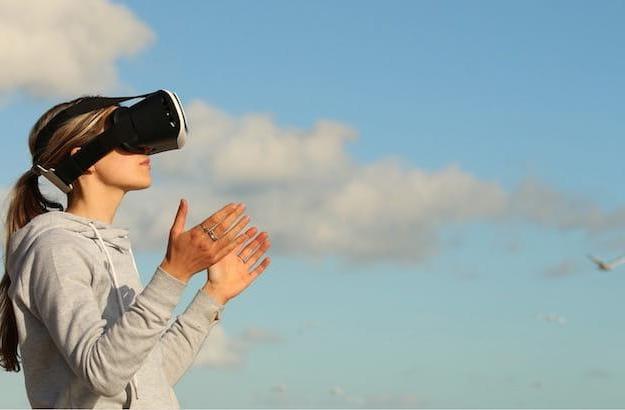

Let's start seeing first what is virtual reality (often abbreviated as VR, Virtual Reality): As I already mentioned in the introduction, VR is a technology of simulated reality which is based on a three-dimensional environment, made on a computer or captured with lenses capable of shooting the scene at 360 degrees, which can be explored by the user using special devices, including viewers, earphones e gloves / controller.
From this it is clear, therefore, that virtual reality is born from combination of software and hardware devices which, together, allow to replicate a virtual space, within which the user can move freely, as if it were a "real" environment.
The viewer and the software that are used for this purpose, keep track of the movements of the user's head and body (I'll explain how later), adapting the perspective and the view to your position, giving back a rather realistic experience.
When it comes to virtual reality, we must be careful not to confuse this technology with the augmented reality (often abbreviated to AR, Augmented Reality) which, on the other hand, enhances the perception of the world around us with a series of contents and information. Clear examples of augmented reality are apps that allow you to virtually "wear" clothes and those that allow you to place furniture in a room before buying it (I told you about it in this other guide).
Virtual reality, on the other hand, is immersive, it isolates the user from the environment that surrounds him and transports him into a three-dimensional space that absorbs him in all respects. Now I hope you have understood the stark difference between VR and AR.
How virtual reality works

Now is the time to actually understand how virtual reality works. As I mentioned in the previous lines, this technology works through the combination of hardware and software tools which, together, allow the user to immerse themselves in a virtual world, sometimes extremely realistic.
To make the experience as real as possible, various technologies are used, such ashead tracking, that is, the tracing of the garment. Using this technology, the viewer detects the direction and head movements of the user wearing the VR headset to determine the scene to be viewed.
Basically, they exist two types of head tracking: the one based onorientation, which simply detects the direction of the rotations of the user's head (e.g. from left to right or from top to bottom), and that based on the position which, on the other hand, detects the movements of the head, associating them also with the movements made by the body, also detecting movements such as the swaying of the torso forward or backward.
As for position-based head tracking, this can be implemented on the viewers in multiple ways: in some cases, tracking takes place thanks to the use of cameras with infrared, which read the data from some sensors, such as the gyroscope.
As regards the VR viewers - those that you have to wear to be "immersed" in the virtual environment -, there are basically two types: those a single display and those a multiple displays, usually equipped with two lenses internal (one for each eye), which are worn on the face as if they were rather voluminous glasses.
PC and console viewers and standalone (i.e. independent from other hardware) are usually equipped with two internal displays, directly housed on the body; those designed to be used in conjunction with mobile devices, on the other hand, do not have internal displays and allow you to integrate the smartphone inside them, transforming it into the display of the viewer itself.
The higher the resolution used by the display in the viewer (which can be integrated or added, as in the case of the viewers in which the smartphone is inserted), the higher the quality of the experience returned by the same. To be clear: a QHD resolution screen will offer a better experience than an FHD or lower resolution display.
When purchasing a VR viewer, you must also pay close attention to the update frequency (o refresh rate) of the images: it is advisable that this is greater than 60 Hz, which minimizes the phenomenon of motion sickness, or the feeling of nausea that is generated by movement in the virtual environment. Once worn, the headset offers the user one stereoscopic vision to the user, which allows you to perceive the sense of depth that characterizes the three-dimensional nature of the virtual environment.
In addition to VR headsets, there are also other devices which can be used together with the latter and which are intended to make the experience as real as possible and even interact with the virtual environment. Among these, there are, for example earphones, which transfer sounds to the user, ei gloves / controller which, instead, are used as input tools (especially in VR video games) to perform movements, give commands, type on virtual keyboards and so on.
There are also some tute VR o cybertute, which envelop the whole body to perform a three-dimensional scan of the same and transfer it to the virtual environment, however they are not yet widespread.
Uses of virtual reality

Given the interesting features and versatility of this technology, the uses of virtual reality they are many. First of all, of course, there is the one related to the world gaming: thanks to virtual reality, in fact, it is possible to enter a video game in first person and enjoy a very high level of immersion.
Virtual reality, however, can also be used in other contexts: just think of educational sector, where VR can allow you to study history, geography, art and many other subjects offering the opportunity to see characters, places and settings that are far from the user both in terms of space and time. This use is usually made in university campus And in the museums.
Even in the environments of work virtual reality can find ample space. Thanks to the use of complex 3D rendering software, for example, it is possible to design, virtually create and explore buildings before even starting to build them, so as to be able to verify their structural solidity and minimize the chances of incurring any design flaws.
In medical field, virtual reality finds an important place in the preparation of particularly complex surgical interventions: before putting his hand to the scalpel, a surgeon can use this technology to practice on the most complex steps of the surgery he will have to perform.
And what about the tourism sector? The use of virtual reality can allow users to virtually "travel" around the world and choose the destination of their next vacation. Tourist agencies, on the other hand, can take advantage of virtual reality to show a preview of the services offered to their potential customers.
Clearly these are just some of the possible uses of virtual reality. In general, however, the use of this technology can potentially find space in any sector: it is only necessary to understand how to exploit it in a useful way.
Virtual reality systems

We conclude this guide with the list of the main ones virtual reality systems currently on the market. If you want to personally experience the immersive experience offered by this technology, all you have to do is choose the viewer that best suits your needs, among those listed below, and buy it. Prices are now quite low compared to a few years ago.
- Oculus Rift - is a viewer equipped with OLED display with resolution equal to 2160 × 1200 pixels and refresh rate a 90 Hz, which offers a field of vision beyond 90 degrees horizontally and 110 degrees diagonal. It must be connected to the computer.
- PlayStation VR - is a viewer with one 5.7 "OLED screen having a resolution of 1920 1080 pixels x, accelerometer e gyroscope to 3 axis and a refresh rate of 90-120Hz. It finds application both in the field of gaming and in the use of multimedia content thanks to Cinema mode with which it is equipped. As easily understood, it should be used in conjunction with a PlayStation 4.
- Oculus Go - available in 32 and 64 GB of internal memory, this viewer is equipped with 2560 × 1440 pixel WQHD screen with a refresh rate of up to 75 Hz, guaranteeing an all in all fluid experience. It is standalone, which means it can be used without being connected to a computer, console or mobile phone.
- HTC Vive - comes with one 2160x1200 pixel OLED screen, with a refresh rate of 90 Hz, a viewing angle of 110 degrees and various sensors, including accelerometer, gyroscope and video camera, necessary for the correct tracking of the user's movements. It must be connected to the PC.
- Samsung Gear VR - Samsung's headset is one of the most popular on the market. Offers a viewing angle of 101 degrees and does not integrate a display (so you have to insert a compatible smartphone inside). The variant SM-R324 It is fully compatible with the following devices: Galaxy S8, S8 +, S7, S7 edge, S6 edge +, S6, S6 edge. The variant SM-R325 it is compatible with the latest Samsung smartphones.
- Google Daydream View - it is a viewer made by Google that offers the possibility of immersing yourself in virtual reality at a decidedly aggressive price. To work, it requires pairing a smartphone that acts as a display and is supported, such as Google Pixel e Google Pixel 2.